Overview
Understanding normal ALT levels by age is critical for evaluating liver function. Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) is an enzyme found mainly in the liver, and its presence in the blood can suggest liver function and potential liver problems. This article will look at typical ALT levels throughout age groups, gender differences, and particular issues, including liver trace results, the cost of the LFT test, and ALT levels in conditions that can result in elevated readings, such as ALT at 116 U/L.
What Is Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT)?
ALT is a liver enzyme that breaks down proteins and can be used to determine liver health in a liver function test (LFT). Elevated ALT levels can indicate liver stress or injury, which is commonly caused by liver disease, drugs, or infections. Knowing the normal ALT levels by age and gender might help you determine whether your liver is functioning correctly.
Normal ALT Levels By Age
ALT levels are typically measured in units per litre (U/L) and can change with age. Here is a breakdown of normal ALT levels by age to help you understand healthy ranges.
- Newborns and Infants (0-1 year): Infant’s ALT levels are frequently higher due to liver development. Typical values range from 13 to 45 U/L.
- Children (1-12 years): ALT levels can range from 10 to 30 U/L. Normal ALT levels by age (pediatric) are generally lower than in newborns; however, they fluctuate with developmental stage.
- Teens (13-18 years): ALT levels stabilize and approach adult levels, often ranging from 10 to 40 U/L.
Adults (19 years and older):
- Normal ALT Levels for Males: Men typically have higher ALT levels than women. Male’s normal ALT levels usually range between 10 and 40 U/L.
- Normal ALT Levels for Females: Women usually have slightly lower ALT levels, ranging from 7 to 35 U/L.
Normal AST And ALT Levels With Age
Another enzyme tested for liver function is aspartate aminotransferase (AST). Normal AST and ALT readings by age help to provide a more complete picture of liver health. ALT is primarily restricted to liver cells, whereas AST can be seen in muscles. A balanced ALT/AST ratio is seen as a good sign.
Gender Differences In ALT Levels
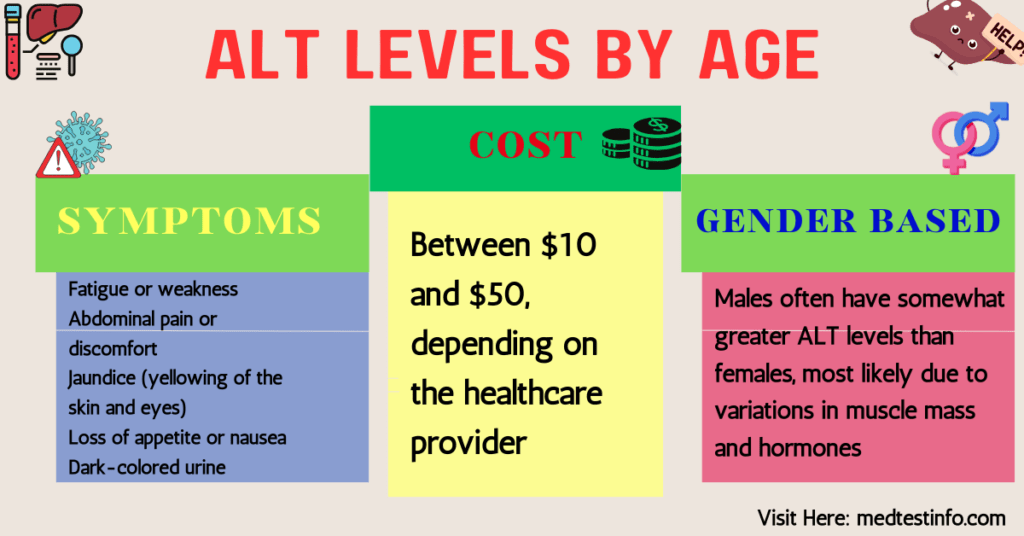
Normal ALT levels by age and gender help evaluate liver function test findings. Males often have somewhat greater ALT levels than females, most likely due to variations in muscle mass and hormones. Understanding these differences might help you estimate liver function more accurately based on gender.
ALT At 116 U/L: Is This Cause For Concern?
An ALT level of 116 U/L is considered high and could suggest liver inflammation or damage. This could be caused by a variety of illnesses, including viral hepatitis, fatty liver disease, or medication side effects. Symptoms of high ALT levels may include exhaustion, stomach pain, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), and dark urine. If the ALT level is exceptionally high, visit a healthcare expert for additional testing and evaluation.
Liver Trace Meaning In Liver Function Test
When trace levels of liver markers or enzymes are found in test results, the term “liver trace” may appear. This may not necessarily imply liver illness, although it can signal slight changes. Liver trace findings may indicate a modest, generally transitory, liver response or a low level of enzyme release.
Symptoms Of Elevated ALT Levels
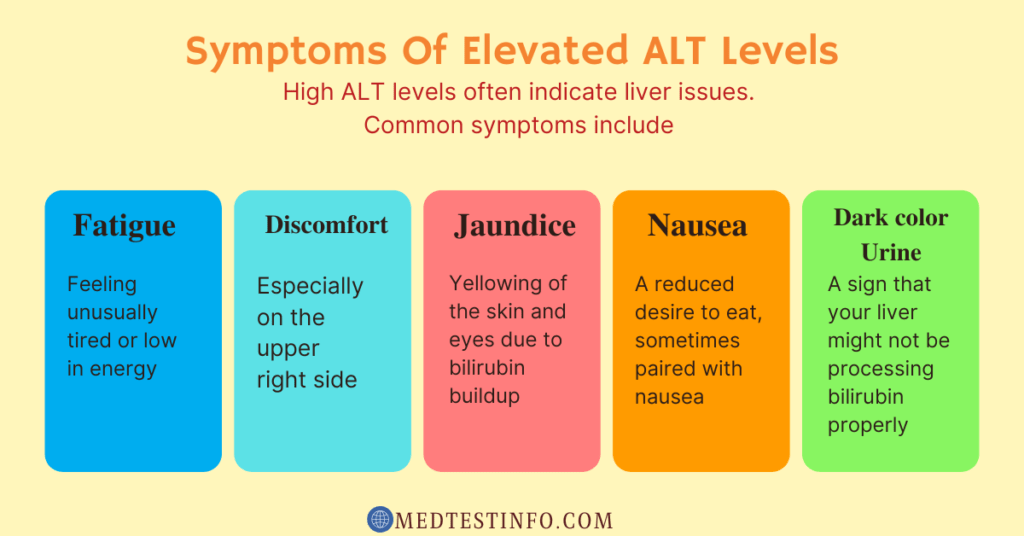
Symptoms associated with increased ALT levels frequently hint at underlying liver problems, such as:
- Fatigue or weakness
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Loss of appetite or nausea
- Dark-colored urine
Your liver may require additional assessment if you have these symptoms and high ALT levels.
What Affects ALT Levels?
ALT levels can fluctuate for a variety of reasons, including:
- Diet and alcohol consumption: Eating high-fat foods and drinking alcohol can elevate ALT levels.
- Medications: Certain medications may cause an increase in liver enzyme levels.
- Exercise: Intense physical exercise might temporarily raise ALT.
How To Maintain Normal ALT Levels
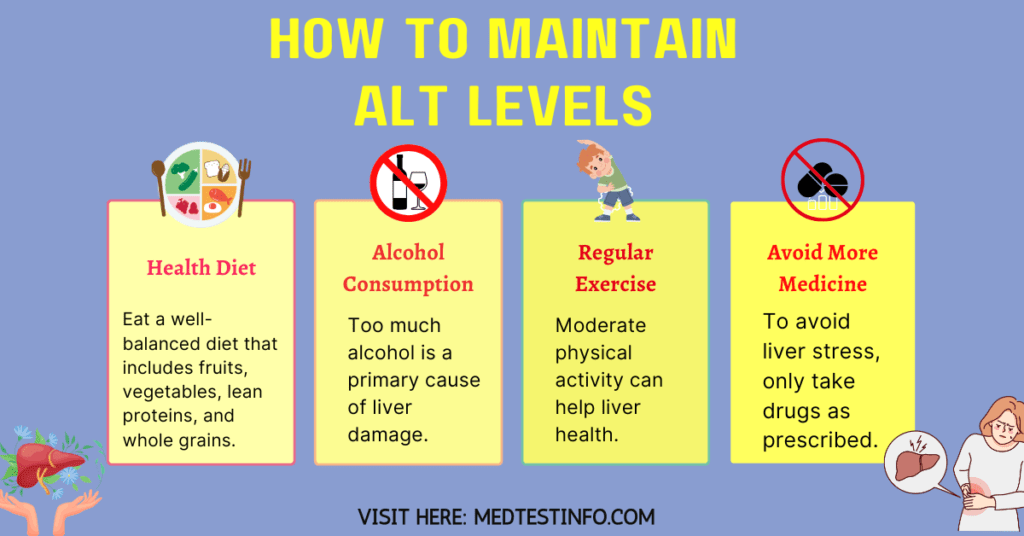
To maintain a healthy liver, make lifestyle choices that promote liver function and prevent injury. Here are some tips for keeping ALT levels in the normal range:
- Healthy Diet: Eat a well-balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Moderate Alcohol Consumption: Too much alcohol is a primary cause of liver damage.
- Regular Exercise: Moderate physical activity can help liver health.
- Avoiding Unnecessary Medicines: To avoid liver stress, only take drugs as prescribed.
The Cost Of LFT Testing And Tube Color Information
A liver function test (LFT) usually costs between $10 and $50, depending on the healthcare provider. LFT tubes, typically green or red, are explicitly designed for serum chemistry assays, such as ALT readings. The tube colour may vary based on the lab protocol; however, these are the most typical colours for liver testing.
Additional Factors In Liver Health Monitoring
Aside from ALT levels, liver function tests may include additional indicators such as bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase. A comprehensive LFT provides a more complete picture of liver health and can aid in the early diagnosis of liver-related problems.
Conclusion
Understanding normal ALT levels by age, gender, and other health parameters is critical for assessing liver function. Elevated ALT levels, such as 116 U/L, require attention and may indicate an underlying problem, especially if symptoms are present. Liver function tests, especially ALT levels, are critical for detecting and monitoring liver disease. Consult a healthcare specialist who can interpret your results concerning your overall health to get the best care.
By being proactive about liver health, you can help prevent problems before they worsen, ensuring normal ALT levels and general well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Take high ALT levels seriously if they exceed the normal range (usually more than 50 U/L for adults) and come with symptoms like fatigue, abdominal pain, jaundice, or black urine. Persistently increased ALT levels may indicate liver inflammation, infection, or more severe liver problems. See a doctor for further assessment and testing if ALT levels remain elevated.
To lower ALT levels, adopt a liver-healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, limiting alcohol use, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and avoiding needless drugs. Certain natural supplements, such as milk thistle or turmeric, may also benefit liver function; however, ask your doctor before beginning any supplement regimen.
Yes, pregnancy can induce increased ALT levels, most commonly due to liver-related pregnancy problems such as preeclampsia, intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy, or HELLP syndrome. If you are pregnant and have high ALT levels, you should discuss this with your doctor, as maintaining liver health during pregnancy is critical for both mother and fetal health.
ALT levels can remain raised for 24 to 72 hours after drinking, depending on how much was consumed and how healthy the liver is. Heavy or chronic alcohol intake might result in persistently elevated ALT values due to liver inflammation or damage. If you see an increase in ALT after drinking, lowering or abstaining from alcohol can help bring levels back down over time.
High ALT levels are not necessarily harmful, but they can be an early sign of liver stress or injury. Mildly high ALT without symptoms may be due to a transient fluctuation. However, if ALT is very high or regularly increased, further testing may be required to rule out underlying illnesses such as fatty liver disease, hepatitis, or medication side effects. Regular monitoring and lifestyle changes can help maintain ALT levels efficiently.


