Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace professional medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare provider for advice regarding your health and medical conditions.
Introduction
The Complete Blood Count (CBC) without differentials, a key player in routine health checks and medical assessments, is a proactive tool for monitoring overall health. This version of the test, which focuses on specific blood indicators rather than categorizing white blood cells as subtypes, is extensively used to measure overall health and monitor blood cell counts. Its role in routine health checks empowers healthcare professionals and individuals to take a proactive and responsible approach to their health.
The Basics Of CBC Without Differentials
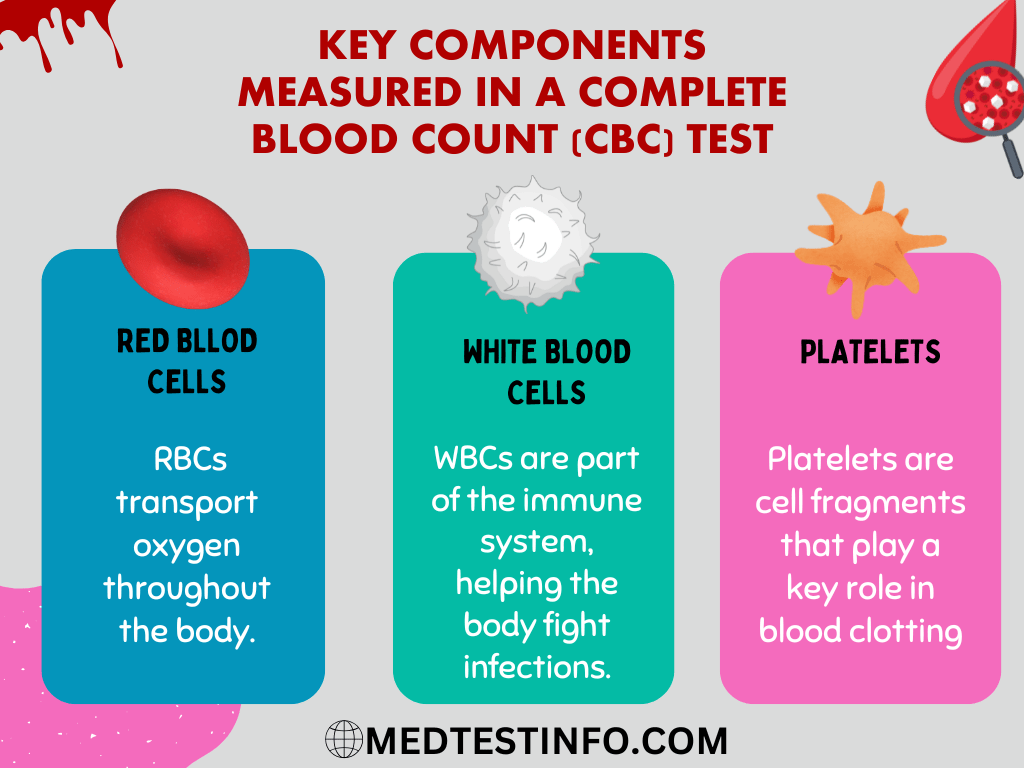
What Does A CBC Without Differentials Measure?
A complete blood count (CBC) without differentials evaluates the key components of blood, offering an overview of your health. This test is largely evaluating:
Red Blood Cells (RBCs): Red Blood Cells (RBCs) deliver oxygen from your lungs to the rest of your body while returning carbon dioxide for exhalation. Low RBC numbers may indicate anaemia, whereas high RBC counts may indicate dehydration or other medical issues.
White Blood Cells (WBCs): WBCs assist the body in fighting infections and play an important part in immunological response. A CBC with differential provides information about several WBC types, whereas a CBC without differential provides a broad WBC count without specificity.
Hemoglobin (Hgb): Hemoglobin (Hgb) is a protein found in red blood cells that is responsible for transporting oxygen. Low haemoglobin levels are a common sign of anaemia.
Hematocrit (Hct): The proportion of blood volume made up of RBCs. It is another excellent test for detecting anaemia and other diseases that impact red blood cells.
Platelets: Platelets are involved in blood clotting, which helps to stop bleeding after an injury. Abnormal platelet counts may indicate clotting abnormalities or bone marrow problems.
This set of measures provides useful insights without requiring a split of WBC types, making it appropriate for general health assessments.
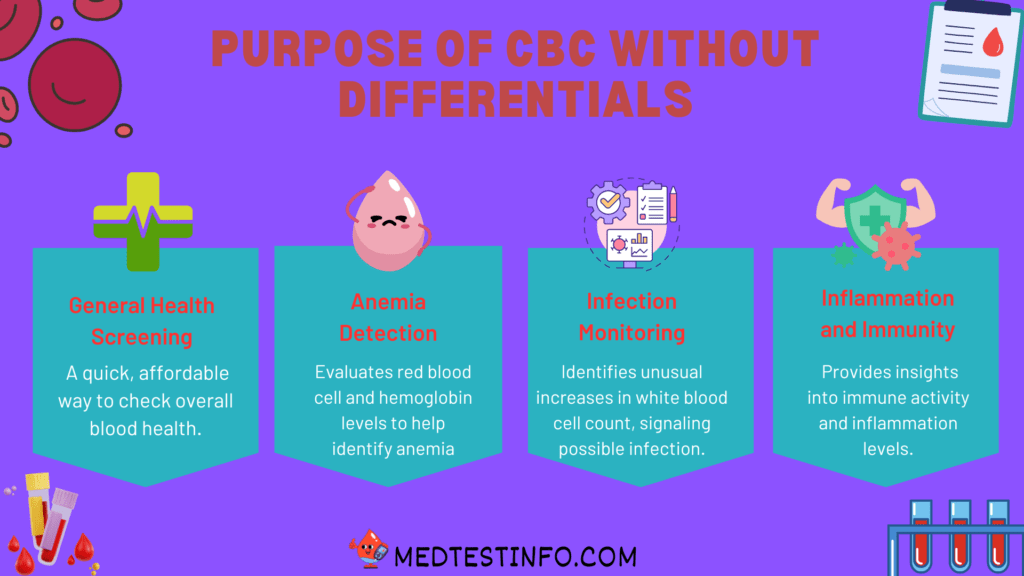
Why Does Doctors Order It?
Doctors frequently order CBCs without differentials to assess overall health during routine visits, look for a variety of illnesses, or monitor existing health issues. This test is very beneficial for identifying symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, and infection. Because a CBC without differential focuses on the key blood indicators, it is effective for diagnosing anaemia, inflammation, or dehydration without the requirement for a differential CBC, which provides a more thorough white blood cell breakdown.
Interpreting the results of a CBC without differential involves comparing the values of each component to the normal ranges. If any value falls outside the normal range, it could indicate a health issue that needs further investigation. For instance, a low RBC count may suggest anaemia, while a high WBC count could indicate an infection. If the results come back abnormal, doctors may order a CBC with differential to get more information.
Differences Between CBC Without And With Differentials
A CBC without differentials offers broad blood cell counts but does not classify white blood cells. A CBC with differentials, on the other hand, divides WBCs into categories such as neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils. This split is useful for identifying specific infections, allergies, and autoimmune diseases.
For example, a high WBC count in a CBC without differentials may indicate an infection; however, a CBC with differentials can determine whether the illness is bacterial or viral, depending on the WBC type. When the purpose is general health assessment or routine monitoring, a basic CBC with no differential is faster, less difficult, and sufficient. On the other hand, if a patient presents with symptoms of a specific infection or autoimmune disease, a CBC with differential may be necessary to provide a more detailed diagnosis.
What Every Value Means
Each component in a CBC without differentials has an impact on overall health, and recognizing these values aids in interpreting results:
Red Blood Cell (RBC) Count: Normal RBC count ranges from 4.7 to 6.1 million cells/µL for men and 4.2 to 5.4 million cells/µL for women. Lower counts may indicate anaemia, but higher counts could indicate dehydration or diseases such as polycythemia.
White Blood Cell (WBC) Count: A normal WBC count ranges from 4,500 to 11,000 cells per µL. An increase may indicate an infection or inflammation, whereas a reduction could indicate an immunological disease.
Haemoglobin (Hgb): Normal haemoglobin levels for men are 13.8-17.2 g/dL, while for women, they are 12.1-15.1 g/dL. Low haemoglobin levels are often indicative of anaemia.
Hematocrit (Hct): Normal hematocrit readings range from 41-50% for men and 36-44% for women. Deviations may indicate anaemia, dehydration, or blood problems.
Platelet Count: Normal platelet count is 150,000-450,000 per µL. Abnormal platelet counts may indicate bleeding diseases or bone marrow abnormalities.
This section helps patients comprehend their results by offering context to numbers that may otherwise appear abstract.
Common Blood Test For Health Checkups
Routine blood tests are vital for preventative healthcare, and one of the most prevalent is a CBC with no differentials. This test can be combined with others, such as the basic metabolic panel, lipid panel, and glucose tests, to provide a comprehensive picture of health. A CBC without a differential is usually sufficient to establish overall health without digging into the intricacies of immunological function.
During routine visits, doctors may use this test to screen for anaemia, detect symptoms of infection, or monitor diseases such as chronic illness. As a fundamental blood test, it establishes a baseline, allowing healthcare providers to monitor changes over time.
Interpretation Of CBC Without Differentials Results
Understanding Results
Interpreting what each component of this test mean for health. Here is a breakdown of the main findings and their normal ranges:
Red Blood Cell (RBC) Count: A low RBC count may indicate anaemia or blood loss, whereas a high count may indicate dehydration or polycythemia.
White Blood Cell (WBC) Count: A WBC count in the usual range (4,500 to 11,000 cells/µL) indicates a healthy immune system. Higher-than-average levels may indicate an infection, inflammation, or stress, whereas lower levels may indicate impaired immunity or specific bone marrow diseases.
Hemoglobin (Hgb): Hemoglobin (Hgb) levels indicate oxygen-carrying capability. Lower levels are frequently associated with anaemia, which can produce symptoms such as weariness and weakness. Elevated haemoglobin levels can sometimes be caused by living at high elevations or smoking.
Hematocrit (Hct): Hematocrit (Hct) is the proportion of blood made up of red blood cells. A lower-than-normal hematocrit indicates anaemia, but higher numbers could indicate dehydration or a red blood cell disease.
Platelet count: Platelets play an important part in blood coagulation. A normal platelet count ranges from 150,000 to 450,000 per µL. Platelet levels might be low or high, indicating a bleeding issue or an inflammatory condition.
Knowing what each parameter represents allows us to better understand the insights of this test provides about general health. If any values fall beyond the typical range, additional research may be required.
Interpreting Abnormal CBC without Differential Results
If CBC without differentials returns abnormal results, it could signal a number of health problems. Here is what certain deviations could mean:
Low RBC or Hemoglobin Levels: Low levels are often connected with anaemia, which a lack of iron, vitamin B12, or folate could cause. Chronic illnesses, kidney disease, and blood loss can all cause low RBC or haemoglobin levels.
High RBC or Hemoglobin Levels: Elevated RBC or haemoglobin counts can result from dehydration or living in a high-altitude environment with low oxygen levels. They could also indicate polycythemia, a disorder in which the body generates an abnormally high number of red blood cells.
Low WBC Count: A low WBC count could indicate immunological weakness, bone marrow abnormalities, or viral infections. People undergoing chemotherapy frequently have low WBC counts due to the chemotherapy’s influence on bone marrow.
High WBC Count: A high WBC count typically implies an infection, inflammation, or immunological response. It could also be a response to physical or emotional stress.
Low Platelet Count: Low platelet count, also known as thrombocytopenia, may indicate a bleeding illness, specific autoimmune diseases, or a bone marrow condition.
High Platelet Count: Elevated platelet counts (thrombocytosis) may indicate chronic inflammation, iron deficiency, or an underlying disease that impairs bone marrow function.
In most cases, abnormal findings do not indicate a serious illness. However, they frequently result in additional testing or monitoring to identify and manage potential health issues.
What Does A CBC Without Differentials Look For?
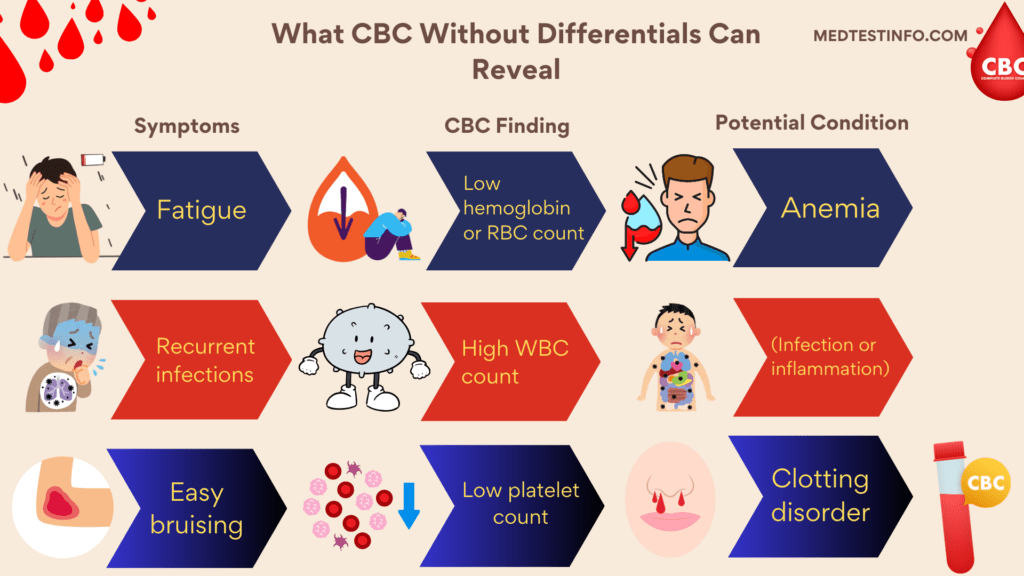
It is routinely used to check for a variety of fundamental health concerns. This test can detect or monitor a variety of conditions, including:
Anaemia: Hemoglobin, hematocrit, and RBC count are important indicators for distinguishing between different kinds of anaemia, which is defined by low red blood cell numbers.
Infections and Inflammation: Although it does not distinguish between white blood cell types, it can indicate whether more research into suspected infections or inflammation is required.
Bleeding or Clotting Disorders: Platelet counts are critical when diagnosing bleeding or clotting issues. Low platelet counts may signal a danger of excessive bleeding, whereas high counts may indicate an inflammatory response.
General Health Monitoring: Gives a fast assessment of overall health as part of routine health checkups, which is important for preventative care and early diagnosis of health problems.
Doctors use this test as a starting point to decide whether more specific tests or treatments are required.
To Detect Anemia
One of the most prevalent applications for a CBC without differentials is to detect anaemia. Anaemia occurs when there are insufficient healthy red blood cells to adequately transport oxygen to the body’s tissues, resulting in weariness, weakness, and shortness of breath. The test measures:
Haemoglobin: Low haemoglobin levels are the primary indicator of anemia.
Hematocrit: Low hematocrit results indicate anemia because they reflect a reduced proportion of red blood cells in the blood.
When low hemoglobin and hematocrit levels are detected, doctors frequently conduct iron studies, vitamin B12, or folate tests to evaluate the type and cause of anemia.
Important Blood Markers To Monitor
Some indicators are especially crucial to monitor over time in individuals undergoing routine health monitoring or treatment for chronic diseases.
Hemoglobin and Hematocrit: Hemoglobin and hematocrit levels should be monitored regularly to detect anemia and track progress after treatment.
White Blood Cell Count (WBC): Tracking WBC counts can help detect early signs of infection or monitor immunological function, especially in people with chronic illnesses or immune-related problems.
Platelet Count: Regular platelet monitoring may benefit patients with known bleeding disorders, clotting concerns, or chronic inflammatory illnesses.
Routine monitoring of these readings can detect changes before symptoms arise, allowing for a more proactive approach to health management.
CBC Without Differentials In Specific Health Areas
For Cardiovascular Health
While this test is not a direct measure of heart function, several markers in the test can reveal factors that influence cardiovascular health. For example:
Hemoglobin and Hematocrit: Low hemoglobin and hematocrit levels may indicate anemia, which can result in diminished oxygen delivery to the heart and other muscles. This puts an additional burden on the heart, especially in people with pre-existing heart issues.
White Blood Cell Count: High WBC counts can indicate inflammation, a key factor in the development of heart disease. Although additional testing is frequently required to measure cardiovascular health, WBC levels provide basic information and can guide further investigation into potential inflammatory conditions.
By tracking these numbers, clinicians and individuals can proactively determine whether additional cardiovascular tests or lifestyle adjustments are required for optimal heart health, empowering them to take control of their health.
To Monitor Chronic Disease
It can be a useful tool for routine monitoring in people with chronic conditions such as diabetes, renal diseases, or autoimmune disorders. This test detects variations in blood cell counts, which could indicate problems or the need for therapy adjustments, thereby aiding in the proactive management of these conditions.
Red Blood Cells: Chronic diseases frequently impact the synthesis and turnover of red blood cells. Monitoring RBC levels over time enables clinicians to identify probable anemia and treat it appropriately.
White Blood Cells and Platelets: Chronic disorders can impact white blood cell and platelet counts. WBC and platelet counts are monitored to assist in managing inflammation and following illness development.
Regular CBC tests offer baseline readings, allowing healthcare providers and individuals to identify and address problems early in chronic disease management, instilling a sense of reassurance and confidence in their management.
In Pregnancy And Prenatal Care
Pregnant women routinely have CBC tests to evaluate both their health and the health of their developing baby. A complete blood count without differentials may reveal critical elements of maternal health:
Haemoglobin and Haematocrit: Anaemia is common during pregnancy due to increased blood volume and a requirement for extra red blood cells. Low hemoglobin and hematocrit values may indicate iron deficiency anemia, which must be treated for proper fetal development and maternal energy levels.
Platelet Count: Some women have a decrease in platelet count during pregnancy, which is known as gestational thrombocytopenia. Monitoring platelet levels helps to avoid difficulties during birth.
CBC tests in prenatal care help diagnose and control disorders that may affect both the mother and the baby, making them an essential part of normal pregnancy examinations.
In Paediatric Health
Pediatricians frequently utilize it to track children’s health, particularly during growth spurts, illness, or developmental phases. In children, the exam provides useful insights into:
Anaemia: Rapid growth and dietary changes put children at risk for iron deficiency anemia. Monitoring hemoglobin and hematocrit levels can help detect anemia early and assist physical and cognitive development.
White Blood Cell Count: Elevated WBC counts in children may indicate infection, which often influences decisions about additional tests or therapies.
CBC tests are a rapid and effective approach for pediatricians to evaluate a child’s overall health and discover disorders that may impair growth and development.
For Geriatric Health Monitoring
As people get older, their blood cell counts fluctuate due to chronic diseases, drugs, and natural aging. A CBC with no differentials can be useful in geriatric care by:
Detecting Anaemia: Anaemia is frequent among the elderly and can be caused by chronic disease, nutritional deficits, or bone marrow abnormalities. Monitoring hemoglobin and hematocrit levels can help manage symptoms such as fatigue and dizziness.
Assessing Immune Health: A high WBC count could indicate an infection, but a low count could indicate immune system weakening, which is prevalent in older persons. Monitoring these counts allows for proactive treatment to avoid or manage health issues.
Routine CBCs help senior individuals maintain their quality of life by addressing blood-related health concerns early on.
In Surgery And Recovery
It is frequently conducted before surgery as part of the preoperative evaluation. Key variables such as hemoglobin, hematocrit, and platelet counts are measured to determine a patient’s preparedness for surgery and reduce the risk of problems.
Hemoglobin and Hematocrit: Haemoglobin and Haematocrit levels must be adequate to ensure the body’s ability to handle blood loss during surgical procedures. If levels fall too low, the procedure may be postponed, or a blood transfusion may be required.
Platelet Count: A low platelet count increases the risk of bleeding during surgery. Monitoring platelet levels allows surgeons to take the appropriate steps to prevent bleeding.
A CBC, which tracks WBC counts during the recovery phase, can help detect infections or problems, making it an important aspect of postoperative treatment.
In Oncology Care
For cancer patients, regular CBC tests are essential to monitor blood cell levels impacted by cancer or its treatments. Chemotherapy and radiation can dramatically impact bone marrow, lowering RBC, WBC, and platelet numbers.
Red and White Blood Cells: Bone marrow suppression therapies typically cause low amounts of red and white blood cells. Monitoring these numbers assists in managing side effects such as tiredness, susceptibility to infection, and overall therapy response.
Platelets: Low platelet counts increase the risk of bleeding, particularly following bone marrow therapies.
Routine CBCs in oncology therapy assist in tracking the effects of treatment, allowing for modifications to doses or supportive therapies to reduce side effects.
In Detecting Dehydration And Hydration Status
It can also reveal hydration levels, particularly via hematocrit readings. This can be particularly useful in managing hydration in at-risk populations such as athletes, elderly people, and those with chronic diseases.
Hematocrit: Elevated hematocrit values may indicate dehydration because RBC concentrations are increased relative to plasma volume. Low hematocrit may suggest overhydration.
Hemoglobin: Dehydration can lead to a modest increase in hemoglobin concentration. Monitoring hydration levels can benefit athletes, elderly people, and people with chronic diseases.
This program aids in the early detection of dehydration, hence preventing problems and improving recovery in at-risk populations.
Assessing Infections And Immune Response
While this test does not differentiate white blood cell types, it can still be used to detect broad illnesses and immunological responses.
White Blood Cell Count: Elevated WBC counts are a sign of infection; even if there is no breakdown, an overall rise shows that the immune system is responding to a potential pathogen.
Platelet Count: Infections can affect platelet levels, which may be reduced during severe or systemic illnesses.
This use of CBCs is useful in emergency care settings or when a rapid assessment is required to rule out infection as a possible cause of symptoms.
For Routine Checkups And Preventive Health
It also provides a quick and thorough picture of blood health. Routine checks may reveal potential issues, allowing for proactive and responsible health management.
Anaemia, infections, and platelet issues: Routine testing detects these diseases early before symptoms appear. Regular monitoring of blood cell counts can detect imbalances and allow for appropriate action.
Health Monitoring for All Ages: From young adults to seniors, routine CBC testing allows healthcare providers to establish baselines, track changes, and identify health issues early.
Including a CBC without differentials in routine checks promotes a proactive approach to healthcare, assisting in the early detection and treatment of common blood-related diseases.
Limitations And When To Consider A CBC With Differentials
While it can provide useful information about overall blood health, but it has significant limitations. Specifically, it provides a general overview of blood cell counts, while a CBC with differentials provides a detailed breakdown of white blood cell (WBC) types, which play important roles in immunological responses. The absence of WBC breakdown in a CBC without differentials indicates that:
Infections: A high WBC count may indicate an infection, although it does not clarify the type of white blood cells implicated. This reduces the ability to distinguish between bacterial, viral, and other diseases.
Chronic Inflammatory Conditions: In autoimmune disorders, a detailed breakdown of WBC types is frequently required to measure immunological activity and identify the particular cells engaged in inflammation.
Because of these limitations, a this test may require additional testing to provide precise immune response information.
CBC With Differentials For Improved Diagnostic Value
The process of CBC with differentials testing involves a blood sample being taken from the patient and then analyzed in a laboratory. Several health problems and scenarios warrant a CBC with differentials over a basic CBC to acquire a more comprehensive understanding of blood cell health:
When it comes to suspected infections, a CBC with differentials is your go-to tool. It can help you distinguish between bacterial and viral causes, providing a clearer path for treatment. For instance, a high neutrophil count often points to a bacterial illness, while an elevated lymphocyte count may suggest a viral infection. This level of detail can significantly enhance your diagnostic accuracy and confidence.
When it comes to managing autoimmune disorders, a CBC with differentials is your ally. Inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus demand sophisticated immune responses, and a CBC with differentials can help you track immune cells, aiding in diagnosis and treatment planning. This level of insight can make your treatment strategies more effective and your patients’ outcomes more positive.
Haematologic disorders: Detailed WBC analysis is required for blood disorders such as leukemia and lymphoma. A CBC with differentials can reveal aberrant cell counts or shapes that are critical for identifying and staging certain diseases.
Choosing a CBC with differentials enables healthcare providers to get the precise information required for accurate diagnosis and therapy.
How WBC Differentials Improve Infection And Inflammation Diagnosis
WBC differentials provide further diagnostic depth by determining the proportions of each WBC subtype. Here is how each cell type helps us comprehend infections and inflammation:
Neutrophils: High neutrophil counts often indicate bacterial infections or acute inflammation. They may also suggest tissue injury or trauma.
Lymphocytes: A high lymphocyte count indicates viral infections or chronic inflammatory disorders. Elevated lymphocytes may also indicate the presence of some blood malignancies.
Eosinophils: Elevated eosinophil counts are frequently related to allergic reactions and parasite infections, providing particular information on immunological responses.
Monocytes and basophils: These cells, albeit less common, play important roles in chronic inflammation and allergy reactions. Changes in their levels can help with autoimmune disease diagnosis and allergy therapy.
A differential test reveals the nature of immune responses by separating WBC types, allowing for more tailored treatment.
Assessing Blood Cancers And Blood Cell Disorders Using Differential Counts
A CBC with differentials is essential for detecting anomalies that could suggest blood cancer or blood cell diseases. For example:
Leukaemia: Abnormally high or low levels of some WBCs can indicate leukemia. A differential can reveal immature or abnormal white blood cells, which are common in leukemia patients.
Anaemia and RBC Disorders: Differential information can help understand some types of anemia, such as those caused by bone marrow disorders, because immature or irregular red cells can disrupt WBC balance.
A differential count provides clarity in patients with suspected blood malignancies or cell abnormalities, allowing hematologists to assess disease progression and design appropriate treatments.
Why CBC With Differentials Is Important For Monitoring Immune Health
When it comes to monitoring immune health, a CBC with differentials is your proactive tool. For immunocompromised individuals, such as those undergoing chemotherapy or living with HIV/AIDS, it’s crucial to regulate immunological health. A CBC with differentials allows you to track treatment effects and conduct infection surveillance, empowering you to take timely actions to protect your patients’ health.
Tracking Treatment Effects: Chemotherapy and other therapies can lower WBC levels, which weakens immunity. Differential counts assist clinicians in determining whether therapy adjustments are necessary to protect immune health.
Infection surveillance: Immunocompromised patients are more susceptible to infections. A differential count aids in the rapid identification of immunological responses, allowing for timely action if an infection occurs.
A CBC with differentials is thus an essential tool for monitoring immunological health in vulnerable populations, allowing for prompt reactions to potential health problems.
Assessing Allergy And Asthma With Differential Counts
Allergies and asthma frequently include specific immunological responses that can be detected with a WBC differential.
Eosinophils and basophils: Elevated eosinophils are prevalent in allergy and asthma patients, indicating an overactive immune system. Basophils, although uncommon, can be raised in chronic allergy disorders.
A CBC with differentials detects these cells, aiding in the diagnosis and management of allergy and respiratory disorders. This allows people to avoid triggers and better control symptoms.
How CBC with Differentials Can Help Manage Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune disorders, such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, frequently include aberrant immune cell function. A complete blood count with differentials provides insights into immunological function, revealing:
Lymphocyte and Monocyte Levels: Abnormal lymphocyte and monocyte numbers are frequently associated with autoimmune flares. Monitoring them allows healthcare providers to alter therapies to minimize inflammation and efficiently manage symptoms.
In the case of autoimmune disease, a differential count aids in the tracking of disease activity, providing data to inform personalized treatment regimens.
Determining The Need For Further Testing Using CBC Results
A CBC with differentials frequently serves as a bridge to additional testing. If differential results reveal atypical patterns, such as significantly higher neutrophils or lymphocytes, or a high eosinophil count in the absence of an allergic reaction, further diagnostic testing (such as cultures, imaging, or biopsies) may be required to investigate the underlying cause.
Differential counts help streamline the diagnostic process by decreasing guesswork and allowing for more targeted, efficient testing.
When Should A Differential Count Be Conducted To Balance Cost And Clinical Utility?
A CBC without differentials is cost-effective and useful for general screening, but a CBC with differentials has a higher diagnostic value in certain conditions. When deciding which test to order, consider the following factors:
Patient Symptoms: In cases of severe infection symptoms, a differential diagnosis is frequently required to assist in determining the cause.
Health History: Differential testing is beneficial for individuals with chronic illnesses or impaired immune systems because their medical demands are complex.
Treatment goals: Differential counts provide personalized information for certain therapies, allowing practitioners to make exact adjustments in care.
Balancing cost and clinical value enables doctors to select the most appropriate test for each patient’s needs.
When A CBC With Differentials Is Recommended
To summarise, while a CBC without differentials is a useful tool for general health monitoring, a CBC with differential counts is required for comprehensive immunological insights. In situations such as infection detection, cancer management, and autoimmune disease monitoring, differential testing provides information that can help guide appropriate treatments.
Understanding whether to use a CBC with differentials allows healthcare providers and patients to make more educated decisions about blood testing, maximizing the diagnostic value of these tests and achieving better health outcomes.
Practical Considerations For Patients
Preparation Steps For A CBC Without Differentials
Preparation for this test is simple because this test usually does not need fasting or any significant dietary changes. However, specific factors can alter test results:
Medication: Some drugs, such as steroids or chemotherapy, might affect blood cell counts. It is critical to inform the healthcare professional about any existing drugs.
Activity Levels: Excessive physical activity before testing can temporarily increase white blood cell counts. Relaxing for 24 hours prior to the test is advised.
Patients who follow these basic measures can ensure the most accurate CBC findings, which will help healthcare providers interpret them correctly.
What To Expect During And After A CBC Without Differentials
A CBC without differential is a rapid and minimally invasive procedure. Patients can expect:
Blood Draw: A tiny amount of blood is taken from a vein, typically in the arm. The technique takes only a few minutes.
Results Timeline: In most situations, CBC results are ready within 24 hours. For urgent circumstances, labs can speed the process and provide results the same day.
Patients frequently obtain their results from their healthcare physician, who explains the relevance of each count to their health.
When Values Are Outside The Normal Ranges
A CBC without differential usually contains three main metrics: red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), and platelets. Here is what patients should understand about reading these values:
Elevated WBC Count: High WBC levels may indicate infection or inflammation, but they can also be caused by stress or drug side effects.
Low RBC Count: This could indicate anemia or persistent blood loss, necessitating additional testing, such as a hemoglobin check, to discover the root cause.
Abnormal Platelet Count: Low platelet counts can suggest a risk of bleeding disorders, while high counts can indicate inflammation or other health problems.
Understanding what each figure represents can help patients and physicians decide whether more tests or lifestyle adjustments are required.
When To Repeat A CBC Without Differentials?
In many circumstances, a single CBC test with no differentials is adequate for a health screening. However, repeat testing may be recommended in some situations:
Monitoring Treatment: Individuals receiving therapy for diseases such as anemia may require follow-up CBCs to monitor their improvement.
Symptom Changes: If new symptoms appear or existing symptoms worsen, a repeat CBC may be required to assess blood health.
Routine Screening: A CBC performed regularly can help evaluate general health in people with chronic illnesses like diabetes or cardiovascular disease.
Consulting with a healthcare provider ensures that repeat testing is consistent with individual health concerns and treatment goals.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Routine CBC Testing
Routine CBC testing has several health benefits, notably in the early diagnosis of diseases. However, it does have limitations:
Benefits: A routine CBC can detect blood problems early on, help manage chronic diseases, and offer general health information.
Drawbacks: Routine testing may miss certain conditions that necessitate differentiated testing, such as immunological or inflammatory diseases.
Weighing the benefits and restrictions with a healthcare professional can help establish how frequently a CBC without differentials is beneficial to each individual’s health.
Cost And Availability Of CBC Testing
Cost can be varies by geography, healthcare provider, and insurance coverage. Here is what patients should consider.
Many health insurance policies cover routine CBCs as part of preventive treatment.
Out-of-Pocket Cost: For people without insurance, the cost is usually reasonable, but prices vary between labs and clinics.
CBC testing is still available to many people through options such as walk-in labs and community health centers, making it a cost-effective tool for monitoring health.
Key Points When Choosing A CBC Without Differentials
To summarise, a CBC without differentials is a simple and informative test for assessing overall health. Here are the main takeaways.
It contains vital information on red and white blood cells, as well as platelets.
While it is less comprehensive than a CBC with differential, it is quite useful for regular screening and first assessments.
Knowing when a CBC with differential is necessary can improve diagnosis accuracy.
Patients can make more educated decisions about blood testing options if they understand the test’s purpose and limits.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is fasting essential for a CBC with no differentials?
Fasting is only required for a CBC with differentials if specifically requested by your healthcare professional.
2. How often should I have a CBC test?
Most people only need annual or biannual CBCs. However, those with persistent health concerns may require more frequent testing.
3. What conditions can CBCs without differentials detect?
It is generally used to detect illnesses such as anemia, infections, and general blood health disorders. However, it may need to be combined with additional tests to make a more specific diagnosis.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a CBC without differentials is an essential test in healthcare, providing valuable information about blood health for both routine and diagnostic purposes. It is more comprehensive than a full CBC with differential and is an important tool for diagnosing general health issues such as anemia and infection. The collaboration between patients and healthcare practitioners in determining the need for a CBC without differential or a differential count is crucial, making them feel involved and part of the decision-making process.
Ultimately, this test empowers individuals to proactively manage their health by providing crucial information that can shape future treatment and lifestyle decisions.


