
Overview
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) can affect anyone, and it is critical to get checked regularly to maintain your own and your partners’ health. However, reading an STD test result might be difficult due to medical language, figures, and words that are not easily comprehended. This article will show you how to read an STD test results using examples, templates, and an explanation of popular terminology.
Regular testing is vital for sexual health, but many people struggle to comprehend the results. This article will help you understand your STD test results, whether they are positive, negative, or confusing, and what steps to take next. We’ll also answer topics like can blood tests show STDs and what “non-reactive” means on STD tests.
Positive Vs. Negative STD Test Results
Understanding your STD test results is essential for taking control of your health decisions. Results are usually seen as positive or negative, but each outcome has unique implications. This is what they indicate:
Positive Results
A positive result shows that an infection is present. A positive chlamydia test result means that the bacteria responsible for chlamydia were found in your sample. In the same way, a positive result for herpes, HIV, or syphilis implies that the testing process has detected the virus or bacteria linked to these conditions. A positive test doesn’t just indicate an infection; it also signals the need for treatment or additional evaluation. You must talk to a healthcare provider immediately if you get a positive result. This will help you manage the situation and keep others safe.
Negative Results
A negative result means that your sample showed no signs of infection. A negative test result for HIV or gonorrhoea indicates that the tests did not detect the pathogens responsible for these infections. It’s essential to remember that just because you get a negative result, it doesn’t necessarily mean you’re entirely free from disease. Testing too soon after exposure—before the infection has had a chance to become detectable—might lead to a false-negative result. Healthcare providers often suggest follow-up testing or retesting after a certain period, tailored to the specific STD and your risk factors.
When you get a positive result, taking action immediately is essential. However, even if the result is negative, it’s wise to approach it carefully. Suppose you think you might have been exposed recently or are experiencing ongoing symptoms. In that case, it’s a good idea to talk to your healthcare provider about additional testing and preventive steps you can take. Getting regular screenings is important, especially if you’re sexually active or have multiple partners. It’s a key step in taking care of your sexual health.
By grabbing the significance of your results and reaching out for timely medical advice, you can take charge of your sexual health and find reassurance.
Example Of A Clean STD Test Result
A clean STD test result means no infections were found in your sample during testing. It’s essential to remember the window period. This is the period right after exposure when an infection remains undetectable. Testing during this period may require follow-up to confirm the results.
STD Test Result Template
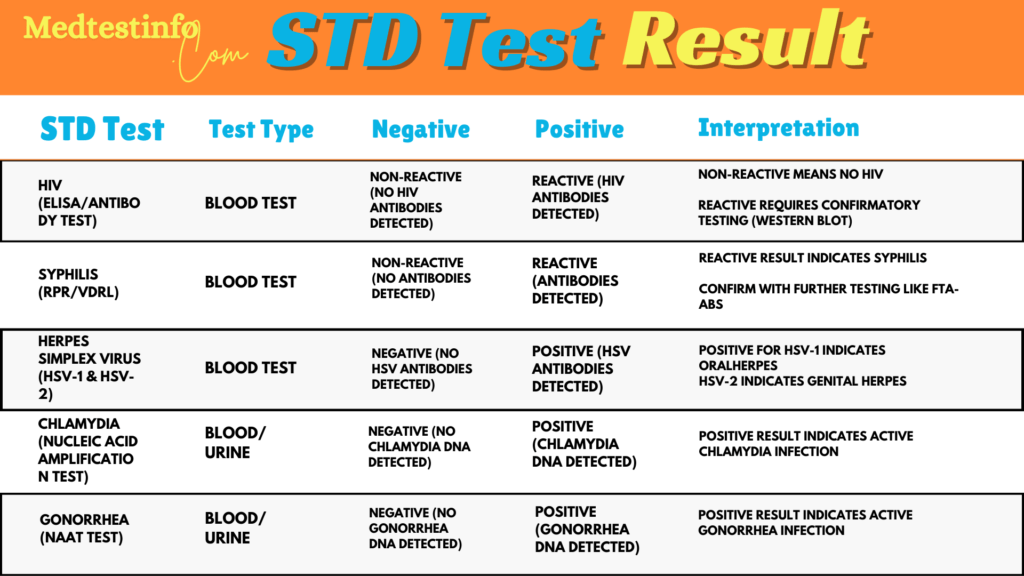
Non-reactive: A non-reactive result for HIV indicates that there are no signs of the virus present. This shows that you are probably not living with HIV. Healthcare providers might suggest getting retested after a few weeks if someone has been exposed recently.
Reactive: A reactive result for syphilis means that the test has found indications of an infection. This doesn’t provide an immediate confirmation of the diagnosis. We need to conduct more tests to eliminate any false positives and understand the stage of the infection.
How To Read Different Types Of STD Test Reports
Understanding your STD test results is essential for catching your health situation and knowing what steps to take for treatment and prevention. There are various ways to test for STDs, such as through blood and urine samples. Every test functions uniquely to pinpoint particular infections. Here’s a straightforward guide to understanding the results of blood and urine STD tests.
Blood Tests For STDs
Blood tests are frequently used to identify the presence of antibodies or antigens linked to particular STDs. An HIV blood test checks for the antibodies our immune system creates in response to the virus. Blood tests play a crucial role in identifying infections such as HIV, syphilis, and herpes, among others. Take a moment to understand what to look for in your blood test results:
Non-reactive:
If your result is non-reactive, no antibodies or antigens were detected in your blood sample. This suggests that you may not have the infection that was being tested for. This means that your sample did not show any signs of HIV antibodies. A non-reactive result is usually seen as a positive outcome, but it’s crucial to keep in mind that some infections, like HIV, might not show up immediately if the test is done too soon after exposure.
Reactive:
A reactive result shows that antibodies or antigens have been found, suggesting an infection is present. If someone receives a reactive result on an HIV test, it indicates that HIV antibodies have been detected in their blood, which suggests that they might be infected with the virus. Following up with confirmatory testing like a Western blot or PCR test is essential when a test returns reactive. This helps to ensure the diagnosis is accurate and provides insight into the stage of the infection.
Indeterminate Or Borderline:
Some blood tests can yield indeterminate or borderline results, meaning the findings may be unclear. To ensure accurate results, additional testing or retesting might be a good idea.
Blood tests are usually more accurate than other methods and can identify infections, even without symptoms. It’s essential to consider retesting, mainly if the initial test was done during the “window period.” This is the phase after exposure when the body might not have had sufficient time to generate detectable levels of antibodies.
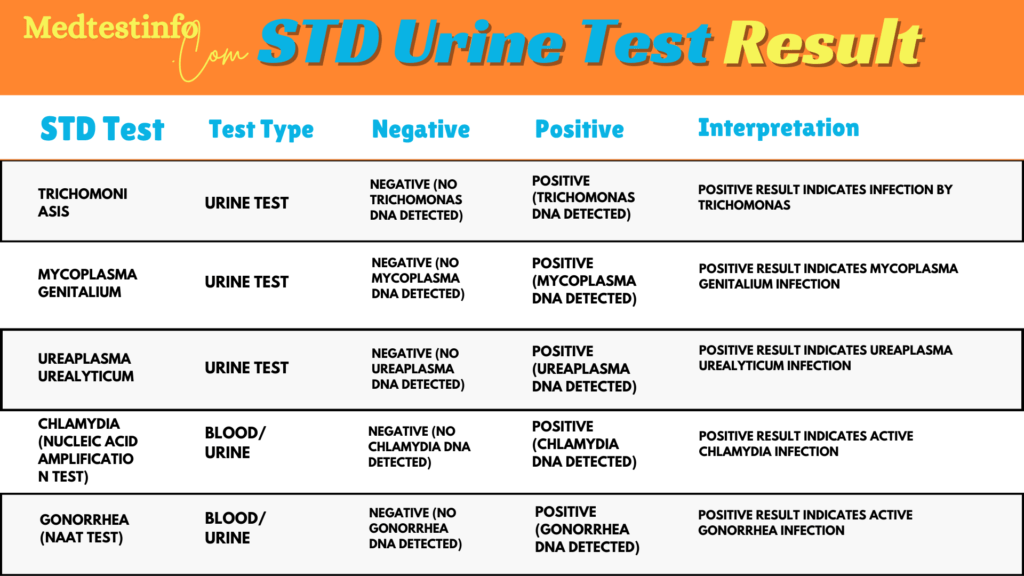
Urine Tests For STDs
Urine tests are commonly utilized to identify bacterial STDs like gonorrhoea and chlamydia. These tests are non-invasive, simple, and frequently used to check for STDs in individuals who might not display any symptoms. Urine samples are examined for the genetic material or microorganisms causing the infections. Let’s take a closer look at what urine test results mean:
Negative:
A negative result from a urine test indicates that the sample showed no signs of bacteria. If you receive a negative result for gonorrhoea or chlamydia, it means that no infection was found in your urine, suggesting that you are probably free from these STDs. It’s important to note that false negatives can happen, especially if the test is done too soon or if the infection is at a stage that makes it more challenging to identify. If you notice any symptoms even after a negative result, it’s essential to contact your healthcare provider for further guidance.
Positive:
A positive result means the test detected some traces of the bacteria responsible for the infection. A positive result for gonorrhoea indicates that Neisseria gonorrhoeae has been detected in the urine, confirming an active infection. If the result is positive, it usually means that antibiotics will be needed for treatment. Depending on the infection, more tests might be necessary to understand how far it has spread or to spot any possible complications.
Urine tests are handy and work well, but they might not catch every STD out there. Some viral infections, such as herpes and HIV, can’t be picked up by urine tests, which means that blood tests are essential for a complete diagnosis.
Key Points To Remember
Understanding your STD test results is essential for taking care of your sexual health. A negative result usually means no infection, but it’s essential to consider things like timing (for example, window periods) when looking at the results. A positive result means that an infection has been found, and it’s essential to seek further medical evaluation and treatment.
Talking to a healthcare provider is essential if you feel uncertain about your results. They can help you understand the findings and guide you on what to do next. Getting tested for STDs regularly is a crucial step in taking care of your sexual health, particularly for individuals with multiple partners or those who may be at a greater risk of exposure.
Staying informed and keeping up with essential tests allows you to take charge of your health and help prevent the spread of infections.
Breakdown By Specific STDs
Chlamydia
Test Type: Urine or swab sample.
Result Interpretation: Positive signifies the infection is present, whereas negative means not. A clean STD test result for chlamydia would be “negative.”
Can you get the STD test result on the same day? Chlamydia tests usually take 1-3 days, although some clinics may provide same-day quick testing.
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus)
Test Type: Blood tests such as ELISA or rapid antibody tests.
Result Interpretation: If your test results are non-reactive, no HIV antibodies were found. What does non-reactive mean on an STD test? It means that the infection was not discovered in your system. However, a negative result is not definitive throughout the 2- to 6-week period following exposure.
Syphilis
Test Type: RPR or VDRL blood tests.
Result Interpretation: A reactive result indicates that syphilis was identified. Follow-up testing may be needed to determine the stage of infection.
Herpes (HSV-1 & HSV-2)
Test Type: Blood test for antibodies or swab test for active sores.Result Interpretation: A positive result suggests the existence of herpes. HSV-1 (oral herpes) and HSV-2 (genital herpes) are standard classifications for results.
Common Terminologies In STD Test Results
What Does Non-Reactive Mean On An STD Test?
A non-reactive result indicates that the test did not detect the presence of the pathogen being tested for. It’s most typically used for HIV and syphilis tests.
What Does Out Of Range Mean On Lab Results?
When you find “out of range” in your test results, it signifies the numbers were higher or lower than the standard reference range. In STD tests, this can signal an aberrant result that warrants further study.
What To Do After Getting Your Result
Positive STD Test Result
If your test results come back positive, here’s what you can do next:
- Let’s schedule an appointment soon to discuss your results and available treatment options.
- Start any prescribed medication or therapy right away to help with the infection. Getting treatment early is essential for handling the condition.
- Let your partners know so they can get tested and receive treatment if needed. This helps keep the infection from spreading.
Staying proactive about your health is crucial. Following your healthcare provider’s guidance helps ensure effective treatment and reduces the risk of further transmission.
Negative STD Result
A negative result usually indicates that no sign of infection was found. In certain situations, it might be essential to conduct follow-up testing:
- For certain infections, such as HIV, receiving a negative result could happen if the test was done too soon. If you have concerns, your healthcare provider might suggest retesting in a few weeks to ensure accurate results.
- Contacting your doctor is a good idea if you’re experiencing symptoms even after a negative result. A negative result sometimes doesn’t necessarily mean that certain infections are ruled out, mainly if the test was conducted in the early stages.
Unclear Or Borderline STD Result
In cases where your test results are unclear or borderline, further steps are needed:
- Retesting might be necessary. Your healthcare provider might recommend extra or follow-up tests to ensure accurate results.
- If you get an unclear or uncertain result, it’s a good idea to talk with your doctor about what to do next and any additional steps you might need to take.
Consulting With Healthcare Providers
Always consult your doctor for any issues or questions about your test findings. They can tell you what to do next, help you understand results that aren’t clear, and offer more tests or treatments if needed.
Getting professional advice helps you make informed decisions about your health and well-being.
Addressing Emotional And Psychological Impacts
Dealing With Positive Outcomes
Getting a positive STD test result can feel really heavy and emotionally challenging to handle. It’s completely normal to experience stress, shame, or fear, and remember, there is support for you. Counseling services offer a supportive environment where individuals can explore their feelings and work towards reducing the negative perceptions linked to their diagnosis. Early professional support can help you through the treatment journey and emotional healing.
Discussing Results With Partners
Having open and honest conversations with your partner is crucial when your STD test results come back positive. Letting others know about your diagnosis helps them take the proper steps or consider getting tested. Engage in the conversation with a sense of calm, prioritizing the well-being and safety of everyone involved. Open and honest communication builds trust and helps minimize the chances of further spread.
Preventing STDs Moving Forward
Even if you receive a negative STD test result, taking these preventive steps can support your long-term sexual health. Consistent testing and mindful practices assist in developing healthier connections and enhance overall well-being.
Conclusion
Interpreting STD test results can be a bit overwhelming, but it’s a crucial part of taking care of your sexual health and overall well-being. Every type of result—non-reactive, out of range, or positive—carries its significance, and grasping these terms is essential for determining the right actions to take next.
A non-reactive result usually indicates that no infection was found, providing peace of mind, but it doesn’t replace the importance of regular screenings. If you get a result outside the normal range, it’s a good idea to follow up with your healthcare provider for more tests or to discuss what it might mean. A positive result shows an infection, which means taking action immediately, like starting treatment and informing partners, is essential.
This guide offers helpful insights to empower you to understand your results and make thoughtful choices about your health. Making regular testing, safe practices, and open communication a priority helps create a healthier future and enhances your overall sexual well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The results of STD tests can differ based on the specific infection being examined. For instance:
Non-reactive or negative results: No signs of infection were found.
Reactive or positive results: Reactive or positive results show that an infection is present.
It’s important to talk to your healthcare provider to understand your specific results better.
Urine tests for STDs, such as chlamydia or gonorrhea, are designed to identify bacteria or genetic material present in your urine.
Negative Results: The test returned negative: no infection was detected in the sample.
Postitive Results: The detection of bacterial DNA suggests an infection is present.
If your test results are positive, you should talk to a doctor for more evaluation and treatment options.
There are several ways to confirm STDs through different diagnostic methods:
Blood Tests: Blood tests are used to find antibodies or antigens, such as those for HIV or syphilis.
Urine Tests: Urine tests can help detect bacterial infections such as gonorrhea and chlamydia.
Swab Tests: Swab tests involve gathering samples from the impacted areas to be analyzed in a lab.
In some situations, we might need additional testing to ensure everything is accurate.
It’s really important to notice symptoms early on. Some typical indicators of STDs are:
1. Something unusual is happening with the discharge from the genitals.
2. It’s a painful feeling when you urinate.
3. Uncomfortable sores or blisters appear on the genitals or mouth.
4. Discomfort or a bothersome sensation in the genital region.
5. Enlarged lymph nodes or symptoms similar to the flu.
It’s important to remember that some STDs can be asymptomatic, so getting tested regularly is crucial for your health.
A Complete Blood Count (CBC) test isn’t designed to identify STDs directly. However, it could show signs of infection, such as a higher white blood cell count, indicating that additional testing for STDs might be necessary.
To get an accurate diagnosis for STDs, you’ll need to undergo certain blood tests or other diagnostic methods.
Certain STDs, such as HIV and Herpes (HSV), can’t be cured, but with the right medication, it’s possible to manage symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. Staying in touch and sticking to your doctor’s recommended treatments can support a healthy life.
Taking care of yourself is key—make sure to practice safe sex and get tested regularly.


