Overview
The MPV (Mean Platelet Volume) blood test is a valuable tool for doctors to evaluate the size of your platelets. This test offers essential insights into your overall well-being, particularly regarding your heart and blood health. But what exactly is MPV in a blood test? This test looks at the size of platelets, the tiny cells that play a crucial role in helping our blood clot. Looking at their size, the MPV test result can uncover hidden health conditions.
Platelets play an essential role in helping to stop bleeding. It might suggest that something needs to be corrected if they are too small or too large. This article will take a closer look at the importance of the MPV blood test, the normal range, and how variations in MPV levels might impact your health.
What Is The Mean Platelet Volume (MPV)?
The MPV test determines the average size of your platelets. Platelets, also known as thrombocytes, are necessary for blood clotting and stopping excessive bleeding following an injury. The average volume of these cells determines the meaning of MPV in blood tests: larger platelets are younger and more active, whereas smaller ones are older and less active. A complete blood count (CBC) commonly includes a blood test for MPV to identify abnormalities in platelet function or generation.
Understanding Platelet Size And Function
Platelets are essential in the body, contributing significantly to blood clotting. These tiny, disc-shaped cells play a crucial role in stopping bleeding when an injury occurs. The MPV test examines the average size of your platelets. Larger platelets tend to be younger and more active, whereas smaller platelets are generally older and less active.
The size of platelets in a blood sample can provide valuable insights into your overall health. For example, when platelets are larger, it can suggest that your body is actively producing platelets to respond to injury or other health conditions.
Platelets are produced by the bone marrow. An issue with platelet production or destruction may suggest the presence of bone marrow disorders. On the other hand, inflammatory conditions can lead to variations in platelet size, as the body may react to inflammation.
Understanding platelet size is not just about clotting. This provides insight into various health conditions, including cardiovascular issues, autoimmune disorders, and cancers. In certain situations, the MPV test result may indicate an increased platelet volume if you live at high altitudes as your body adjusts to the reduced oxygen levels.
The MPV test offers essential information regarding your platelet health. It assists doctors in detecting potential problems at an early stage.
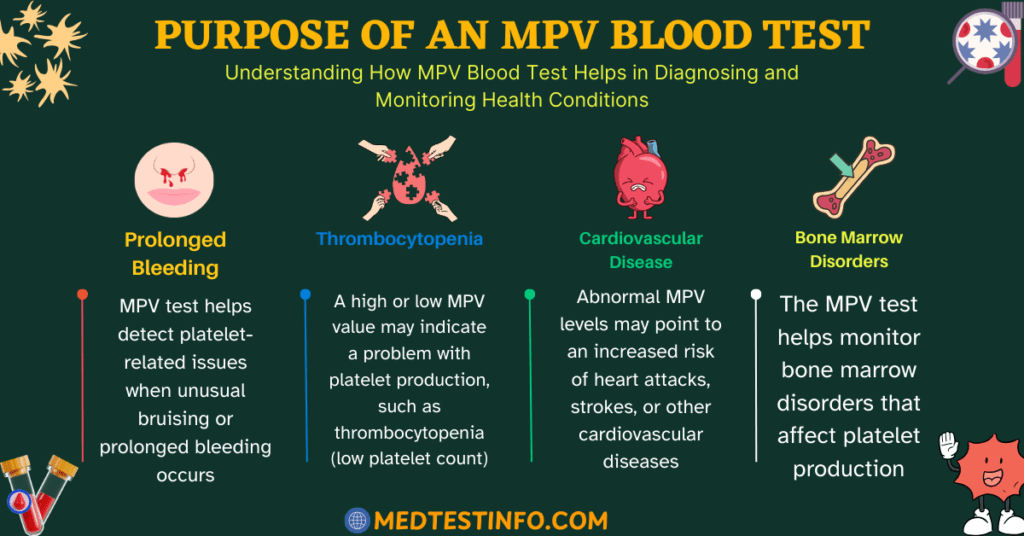
What Is The Purpose Of An MPV Blood Test?
Healthcare providers use an MPV (platelet size) test to identify or monitor diseases that impact platelet production and activity. Abnormal MPV levels may indicate a higher risk of clotting abnormalities or bleeding complications. It is usually used for:
1. Examine unusual bruises or prolonged bleeding.
2. Monitor for problems like thrombocytopenia (low platelet count).
3. Determine the risk of cardiovascular disease, such as heart attacks or strokes.
4. Keep track of disorders involving the bone marrow, which creates platelets.
Normal Range Of MPV
The MPV blood analysis is a valuable diagnostic tool that provides medical professionals with an understanding of the size and health of platelets. The normal range for MPV generally falls between 7.5 and 12.0 femtoliters (fL), but remember that this can differ based on the laboratory and the patient’s age and gender. The MPV test result provides important information about platelet health, essential for blood clotting. It’s commonly paired with other blood markers, like platelet count, to understand overall blood health better.
Abnormal MPV levels might indicate potential health issues like bone marrow disorders or inflammatory conditions, which can influence platelet production. When healthcare providers analyze a blood sample, they can determine if platelet abnormalities might affect clotting issues or other health concerns.
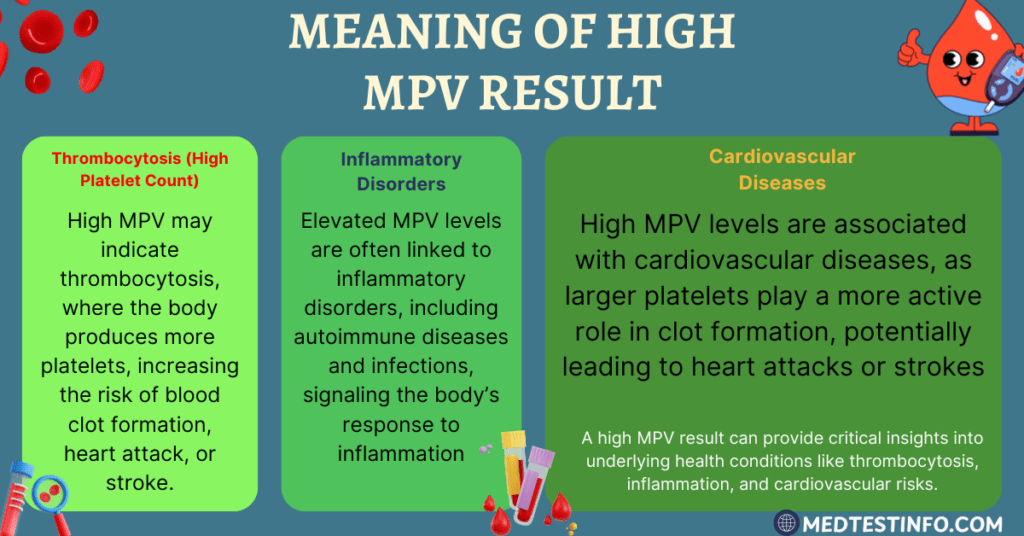
What Does High MPV Mean On A Blood Test?
When the MPV rises, it can increase platelet production, implying that the body responds to a demand for clot formation or platelet replenishment. Conditions like these are often associated with higher MPV results.
1. Thrombocytosis: Thrombocytosis is an unusually high platelet count that raises the risk of clot formation, heart attack, or stroke.
2. Inflammatory Disorders: High MPV levels can indicate inflammation in the body, which is commonly associated with autoimmune disorders or infections.
3. Cardiovascular Diseases: Studies have found that elevated MPV levels in blood tests can predict heart attacks and other cardiovascular events because bigger platelets are more active in clot formation.
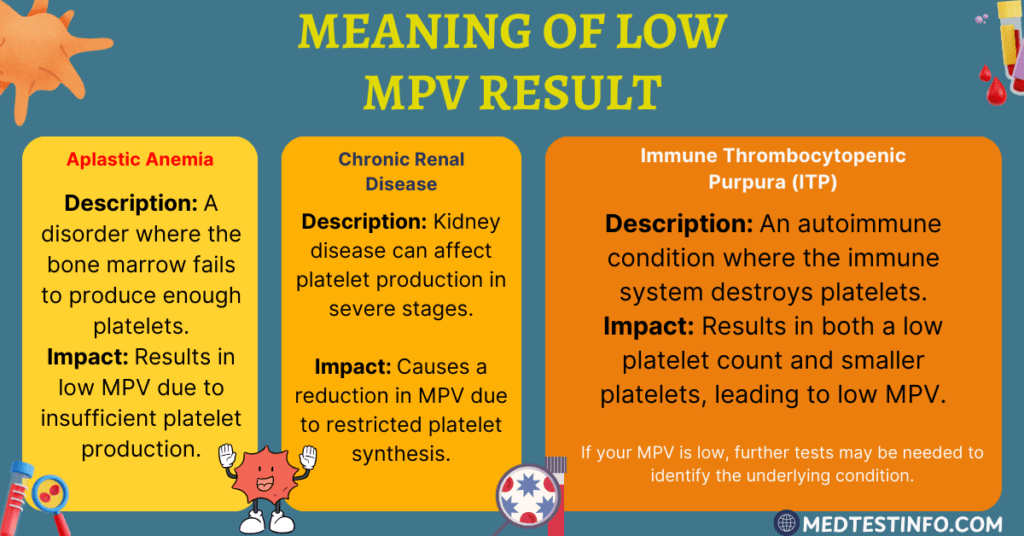
What Does Low MPV Mean On A Blood Test?
On the other hand, low MPV blood test results suggest smaller-than-average platelets, which may signal bone marrow function issues or platelet destruction. Low MPV has several causes, including:
1. Aplastic anemia: Aplastic anemia is a disorder in which the bone marrow fails to make sufficient platelets.
2. Chronic renal disease: In severe stages, renal disease can reduce MPV due to restricted platelet synthesis.
3. Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP): A condition in which the immune system attacks and destroys platelets, causing a reduction in both platelet count and size.
How Is An MPV Blood Test Performed?
The simple procedure involves drawing blood, usually as part of a Complete Blood Count (CBC). A small blood sample is taken from a vein, typically in your arm; no special preparation is necessary. Once in the lab, the test measures the average size of your platelets, providing essential insights into possible health conditions. This testing helps evaluate platelet function and can reveal abnormalities, such as enlarged platelets, which may suggest problems with blood clotting or potential bone marrow disorders.
Interpreting The MPV Results
MPV (Mean Platelet Volume) results are consistently analyzed alongside other blood parameters, such as platelet count, to understand potential health conditions better. A high MPV result and a low platelet count may indicate immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP), where the immune system attacks the platelets. On the other hand, a high MPV with an increased platelet count could suggest inflammatory conditions or complications related to blood clotting, such as thrombocytosis. This scenario indicates that the platelets may be larger and more active in some instances, which could contribute to clot formation. After reviewing these results, your doctor may recommend additional tests to identify or rule out any blood or bone marrow disorders.
Factors That Can Influence MPV Levels
There are several factors that can affect your MPV levels, such as:
1. Age and Gender: MPV levels vary with age and between men and women.
2. Medications: Aspirin and anticoagulants can alter MPV readings, so tell your doctor about any medications you take.
3. Chronic medical conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, and inflammation, can potentially cause variations in MPV levels by affecting platelet synthesis and turnover.
4. Lifestyle Factors: Due to the body’s response to inflammation, unhealthy behaviors are associated with higher MPV levels. Diet, smoking, and alcohol usage can all influence MPV levels.
MPV Blood Test And Cardiovascular Health
MPV test is an important tool for determining cardiovascular risk. According to research, people with raised MPV levels in blood tests are more likely to have blood clots, heart attacks, or strokes. Larger platelets are more reactive and clump more easily, resulting in clots that can block blood vessels. Regular MPV monitoring, particularly in people with recorded heart disease or those at risk, can help prevent potentially fatal cardiovascular events.
MPV In Pregnancy And Its Implications
MPV levels may fluctuate during pregnancy due to hormonal changes and increased blood volume. However, drastically elevated MPV findings during pregnancy could suggest issues including preeclampsia or gestational diabetes. Low MPV test results during pregnancy may indicate anemia or other blood abnormalities, necessitating further study to safeguard the health of both mother and baby.
MPV And Chronic Disease
Chronic disorders can have a significant impact on MPV blood test outcomes. For example:
1. Diabetes: Diabetics are more likely to develop cardiovascular issues; hence, they frequently have elevated MPV levels.
2. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Patients with CKD may have reduced MPV levels due to platelet dysfunction.
3. Autoimmune diseases, such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, can change MPV levels because of persistent inflammation and immune system activity.
New Research And Developments In MPV
Recent studies have looked into novel ways to use the results of MPV tests to predict various health outcomes.
1. Cancer: Elevated MPV levels have been related to some forms of cancer, with bigger platelets potentially contributing to tumor growth and metastasis.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI): Doctors are using artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze trends in MPV lab test results, which helps them more accurately predict the development of the disease.
3. COVID-19: Studies have found that blood tests for MPV findings can help predict the severity of COVID-19, with greater MPV levels indicating worse outcomes.
Conclusion
The MPV blood test is important for detecting and controlling various health issues, including cardiovascular and autoimmune diseases. Whether MPV levels are high or low, they provide significant information about your overall health and platelet function. Regular testing and monitoring can help spot any health problems early, allowing prompt intervention and treatment.
Patients who are concerned about their MPV blood test results should speak with a healthcare provider who can interpret the results in light of their general health and prescribe appropriate follow-up tests or therapies.


